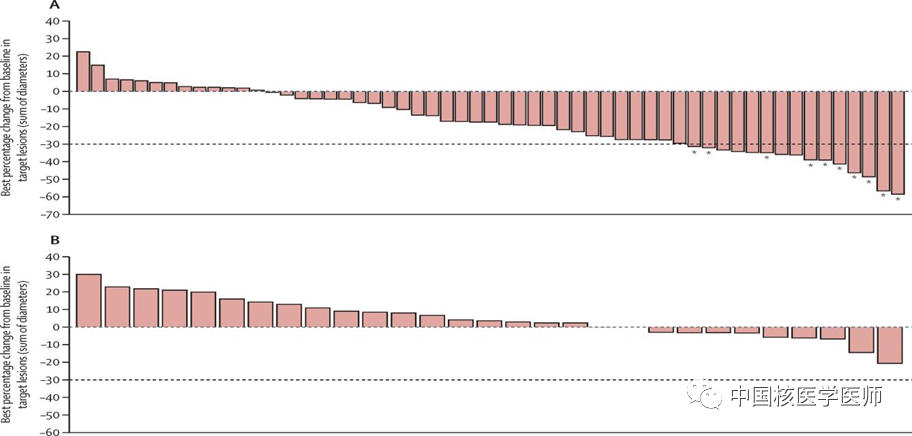
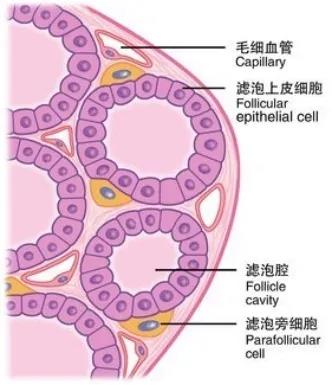
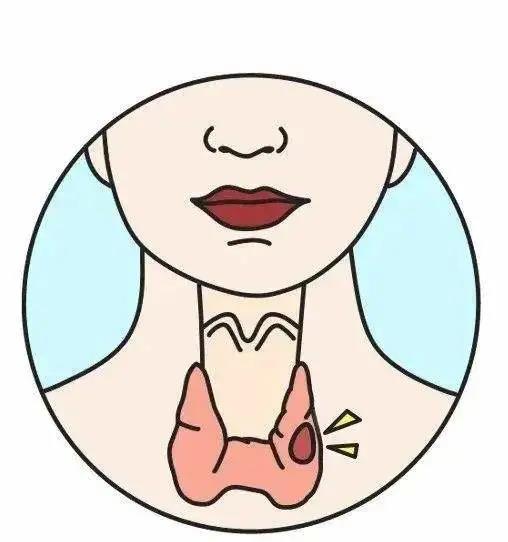
参考文献N2u帝国网站管理系统
(在框内滑动手指即可浏览)N2u帝国网站管理系统
N2u帝国网站管理系统
[1] 日本内分泌外科学会.日本甲状腺外科学会編甲状腺腫瘍診療ガイドライ2018[J]日本内分泌·甲状腺外科学会雑誌,2018,35(suppl 3):1-88. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11226/jaesjsts.35.Supplement3 G1-G88.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[2] Ito Y,Miyauchi A,Oda H,et al.Appropriateness of the revised Japanese guidelines' risk classification for the prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a RETrospective analysis of 5,845 papillary thyroid carcinoma patients[J].Endocr J,2019,66(2):127-134.DOI:10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0061.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[3] Yamazaki H,Masudo K,Rino Y.Migration of risk classification between the jaes versus ata guidelines for papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].World J Surg,2023,47(7):1729-1737.DOI:10.1007/s00268-023-06976-9.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[4] Ito Y,Miyauchi A,Yamamoto M,et al.Subset analysis of the Japanese risk classification guidelines for papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].Endocr J,2020,67(3):275-282.DOI:10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0387.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[5] Horiguchi K,Yoshida Y,Iwaku K,et al.Position paper from the Japan Thyroid Association task force on the management of low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (T1aN0M0) in adults[J].Endocr J,2021,68(7):763-780.DOI:10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0692.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[6] Sugitani I,Ito Y,Takeuchi D,et al.Indications and strategy for active surveillance of adult low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: consensus statements from the Japan Association of Endocrine Surgery Task Force on management for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma[J].Thyroid,2021,31(2):183-192.DOI:10.1089/thy.2020.0330.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[7] Ito Y,Miyauchi A,Fujishima M,et al.Thyroid-stimulating hormone, age, and tumor size are risk factors for progression during active surveillance of low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in adults[J].World J Surg,2023,47(2):392-401.DOI:10.1007/s00268-022-06770-z.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[8] Nagaoka R,Ebina A,Toda K,et al.Multifocality and progression of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma during active surveillance[J].World J Surg,2021,45(9):2769-2776.DOI:10.1007/s00268-021-06185-2.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[9] Chou R,Dana T,Haymart M,et al.Active surveillance versus thyroid surgery for differentiated thyroid cancer: A systematic review[J].Thyroid,2022,32(4):351-367.DOI:10.1089/thy.2021.0539. N2u帝国网站管理系统
[10] Fujishima M,Miyauchi A,Ito Y,et al.Active surveillance is an excellent management technique for identifying patients with progressive low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma requiring surgical treatment[J].Endocr J,2023,70(4):411-418.DOI:10.1507/endocrj.EJ22-0559.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[11] Oda H,Miyauchi A,Ito Y,et al.Incidences of unfavorable events in the management of low-risk papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid by active surveillance versus immediate surgery[J].Thyroid,2016,26(1):150-155.DOI:10.1089/thy.2015.0313.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[12] Sasaki T,Miyauchi A,Fujishima M,et al.Comparison of postoperative unfavorable events in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma: immediate surgery versus conversion surgery following active surveillance[J].Thyroid,2023,33(2):186-191.DOI:10.1089/thy.2022.0444.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[13] Oda H,Miyauchi A,Ito Y,et al.Comparison of the costs of active surveillance and immediate surgery in the management of low-risk papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid[J].Endocr J,2017,64(1):59-64.DOI:10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0381.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[14] Kazusaka H,Sugitani I,Toda K,et al.Patient-reported outcomes in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma: cross-sectional study to compare active surveillance and immediate surgery[J].World J Surg,2023,47(5):1190-1198.DOI:10.1007/s00268-022-06786-5.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[15] Ito Y,Masuoka H,Fukushima M,et al.Excellent prognosis of patients with solitary T1N0M0 papillary thyroid carcinoma who underwent thyroidectomy and elective lymph node dissection without radioiodine therapy[J].World J Surg,2010,34(6):1285-1290.DOI:10.1007/s00268-009-0356-0.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[16] Ito Y,Kihara M,Takamura Y,et al.Prognosis and prognostic factors of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma requiring resection of recurrent laryngeal nerve due to carcinoma extension[J].Endocr J,2012,59(3):247-252.DOI:10.1507/endocrj.ej11-0355.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[17] McCaffrey TV,Bergstralh EJ,Hay ID.Locally invasive papillary thyroid carcinoma: 1940-1990[J].Head Neck,1994,16(2):165-172.DOI:10.1002/hed.2880160211.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[18] Alexander EK,Pearce EN,Brent GA,et al.2017 guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and the postpartum[J].Thyroid,2017,27(3):315-389.DOI:10.1089/thy.2016.0457.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[19] Carling T,Carty SE,Ciarleglio MM,et al.American Thyroid Association design and feasibility of a prospective randomized controlled trial of prophylactic central lymph node dissection for papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].Thyroid,2012,22(3):237-244.DOI:10.1089/thy.2011.0317.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[20] Kim BY,Choi N,Kim SW,et al.Randomized trial of prophylactic ipsilateral central lymph node dissection in patients with clinically node negative papillary thyroid microcarcinoma[J].Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol,2020,277(2):569-576.DOI:10.1007/s00405-019-05702-3. N2u帝国网站管理系统
[21] Lee DY,Oh KH,Cho JG,et al.The benefits and risks of prophylactic central neck dissection for papillary thyroid carcinoma: prospective cohort study[J].Int J Endocrinol,2015,2015:571480.DOI:10.1155/2015/571480.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[22] Viola D,Materazzi G,Valerio L,et al.Prophylactic central compartment lymph node dissection in papillary thyroid carcinoma: clinical implications derived from the first prospective randomized controlled single institution study[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2015,100(4):1316-1324.DOI:10.1210/jc.2014-3825.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[23] Sippel RS,Robbins SE,Poehls JL,et al.A randomized controlled clinical trial: no clear benefit to prophylactic central neck dissection in patients with clinically node negative papillary thyroid cancer[J].Ann Surg,2020,272(3):496-503.DOI:10.1097/SLA.0000000000004345.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[24] Ahn JH,Kwak JH,Yoon SG,et al.A prospective randomized controlled trial to assess the efficacy and safety of prophylactic central compartment lymph node dissection in papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].Surgery,2022,171(1):182-189.DOI:10.1016/j.surg.2021.03.071.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[25] Sanabria A,Betancourt-Agüero C,Sánchez-Delgado JG,et al.Prophylactic central neck lymph node dissection in low-risk thyroid carcinoma patients does not decrease the incidence of locoregional recurrence: A meta-analysis of randomized trials[J].Ann Surg,2022,276(1):66-73.DOI:10.1097/SLA.0000000000005388.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[26] Alsubaie KM,Alsubaie HM,Alzahrani FR,et al.Prophylactic central neck dissection for clinically node-negative papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].Laryngoscope,2022,132(6):1320-1328.DOI:10.1002/lary.29912.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[27] Ito Y,Higashiyama T,Takamura Y,et al.Risk factors for recurrence to the lymph node in papillary thyroid carcinoma patients without preoperatively detectable lateral node metastasis: validity of prophylactic modified radical neck dissection[J].World J Surg,2007,31(11):2085-2091.DOI:10.1007/s00268-007-9224-y.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[28] Sugitani I,Fujimoto Y,Yamada K,et al.Prospective outcomes of selective lymph node dissection for papillary thyroid carcinoma based on preoperative ultRASonography[J].World J Surg,2008,32(11):2494-2502.DOI:10.1007/s00268-008-9711-9.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[29] Ito Y,Miyauchi A,Kudo T,et al.The effectiveness of prophylactic modified neck dissection for reducing the development of lymph node recurrence of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].World J Surg,2017,41(9):2283-2289.DOI:10.1007/s00268-017-4023-6.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[30] Yamazaki H,Sugino K,Katoh R,et al.Outcomes for minimally invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma in relation to the change in age stratification in the AJCC 8th edition[J].Ann Surg Oncol,2021,28(7):3576-3583.DOI:10.1245/s10434-020-09397-3.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[31] Yamazaki H,Katoh R,Sugino K,et al.Encapsulated angioinvasive follicular thyroid carcinoma: prognostic impact of the extent of vascular invasion[J].Ann Surg Oncol, 2022, 29(13):4236-4244.DOI:10.1245/s10434-022-11401-x.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[32] Ito Y,Hirokawa M,Masuoka H,et al.Prognostic factors for follicular thyroid carcinoma: the importance of vascular invasion[J].Endocr J,2022,69(9):1149-1156.DOI:10.1507/endocrj.EJ22-0077.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[33] Zhang J,Gu P,Huang D,et al.Surgical selection and prognostic analysis in patients with unilateral sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma[J].Langenbecks Arch Surg,2022,407(7):3013-3023.DOI:10.1007/s00423-022-02591-9.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[34] Ma SH,Liu QJ,Zhang YC,et al.Alternative surgical strategies in patients with sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma: Long-term follow-up[J].Oncol Lett,2011,2(5):975-980.DOI:10.3892/ol.2011.344.N2u帝国网站管理系统
[35] Sugitani I,Hasegawa Y,Sugasawa M,et al.Super-radical surgery for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: a large cohort study using the Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma Research Consortium of Japan database[J].Head Neck,2014,36(3):328-333.DOI:10.1002/hed.23295.N2u帝国网站管理系统